Strengthening the Grid With Transmission
America’s electric grid, formed in the early part of the 20th century, transformed the United States into an economic powerhouse. However, today 70% of our power lines are more than 30 years old, and the way that power is generated and where energy resources are located has evolved. With an increasing amount of weather-related power outages, more renewables on the grid, and the rapid transition towards the electrification of transportation, the time has come to modernize our antiquated electrical grid.
Grid United develops new long-distance transmission lines to make America’s power grid more reliable and efficient.
Grid United is advancing transmission projects in strategic locations.
THE ADVANTAGES OF TRANSMISSION
Reliability
New transmission capacity, particularly interregional transmission lines, provides black start power or emergency power during extreme weather events. Additionally, interregional transmission lines help mitigate the effects of extreme weather events by allowing new generation to be imported from other areas that are not affected by extreme weather.
Efficiency
New transmission capacity results in cost savings, because new transmission capacity allows power that would otherwise contribute to congestion to be shifted to serve new customers. As this tool showcases, power prices between regions can differ dramatically. Transmission lines are open to all sources of electrical power generation.
Recent reports describe the benefits of transmission buildout.
Understanding Direct Current Technology
Grid United utilizes direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) technology depending on the use case for each project. DC is the preferred technology for moving large amounts of power across long distances. DC results in higher overall efficiency and reliability than an AC system moving the same amount of power.
The Advantages of DC
More
Efficient
Lower
Cost
Higher efficiency means a lower transmission cost, resulting in overall lower electricity costs for consumers.
Improved
Reliability
DC transmission can enhance system stability, allow the operator complete control over power flow, and facilitate the integration of energy from different resource areas.
Smaller
Footprint
Due to a higher efficiency, DC transmission lines can move more power in a given right of way, reducing the need for multiple rights of way and allowing for a smaller footprint.
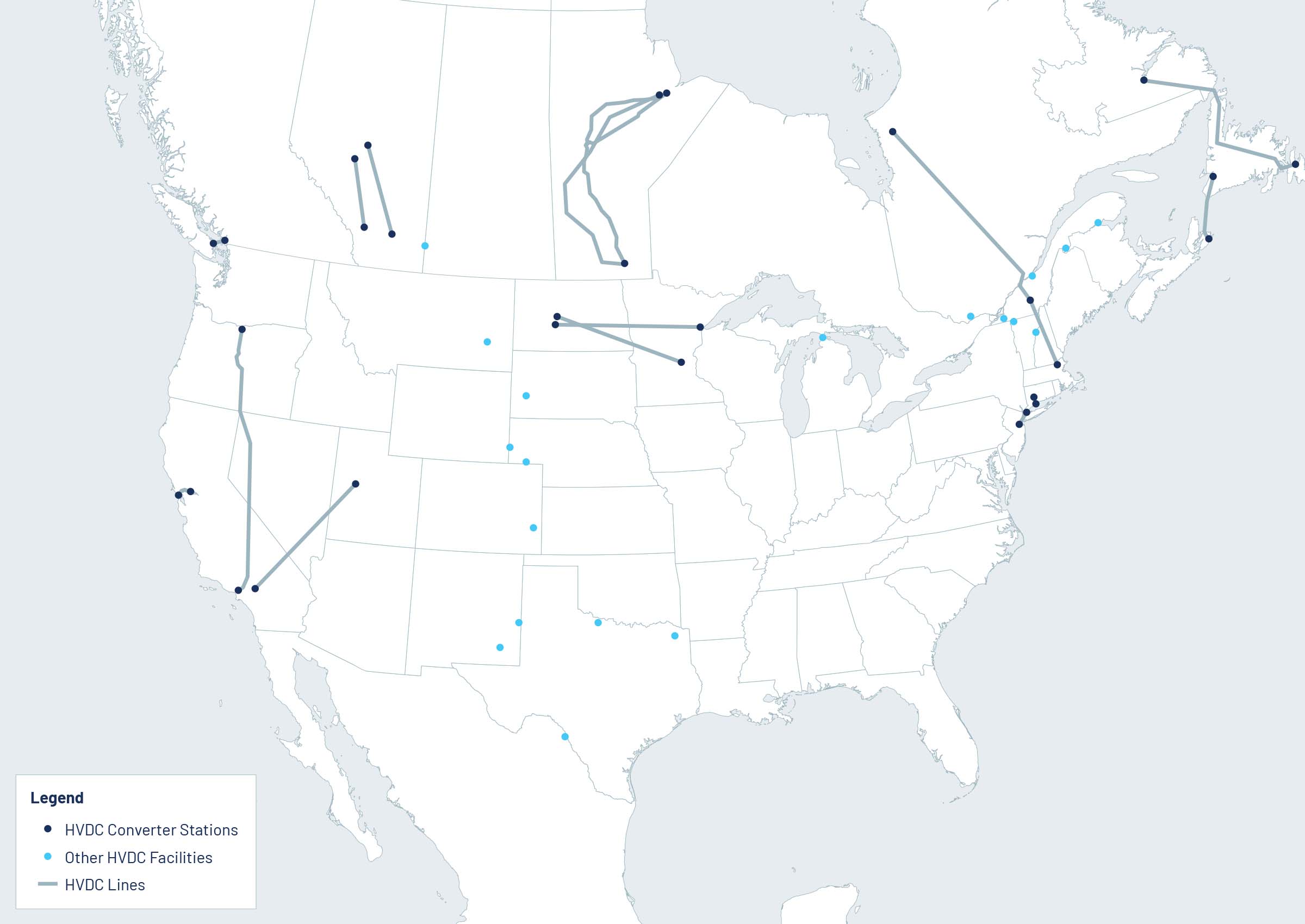
Currently there are more than 20 DC transmission facilities in the United States and more than 35 DC transmission facilities across the North American grid, as indicated in the map below.